Compared with traditional machining methods, rapid Tooling (RT) is a process that using Rapid prototyping techniques with conventional tooling process to produce a mold quickly from CAD data in less time and at a lower cost. Rapid Tooling can act as a bridge to production injection molded parts.
Conventional tooling cost can be well useful just when the production quantity is massive. Along with the various requirement from different product development companies, the way to produce tooling quicker and more economically, especially for small quantity manufacturing becomes more and more popular and significant. Additionally, in the product development cycle, we always requires some fast tooling to produce a small quantity of parts for functional tests, samples for marketing, evaluation purpose, or production process design. Therefore, RT becomes more and more important to nowadays manufacturing industry.
Generally, in my opinion, rapid tooling should include silicone mold vacuum casting and soft metal tooling & molding.
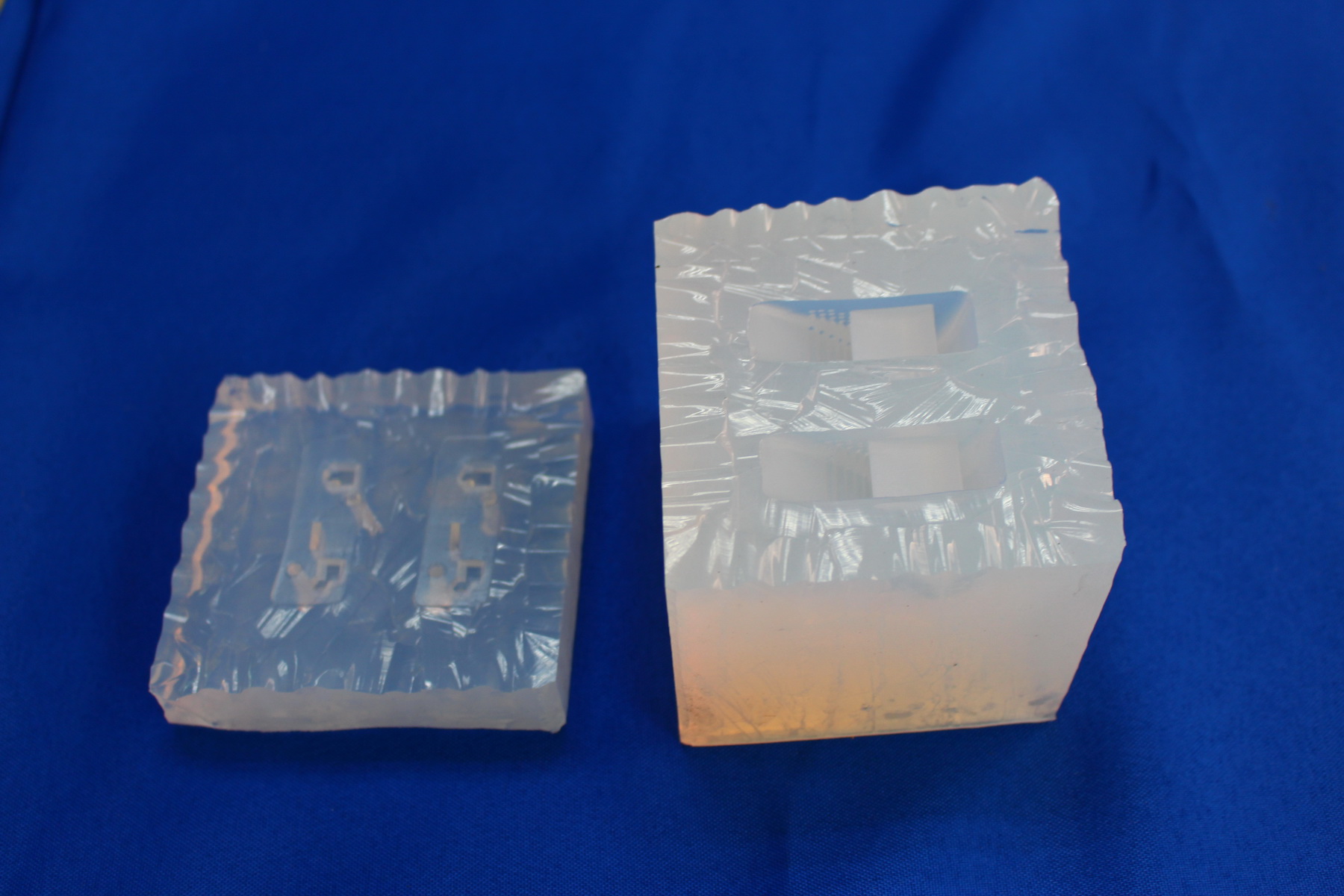
Vacuum casting, helps in getting a small quantity of plastic pieces with much less time and cost of injection molded components. The method uses cast silicone molds made with a master model created by stereolithography (SLA) typically. Silicone material is cast around the carefully developed master model, partially under vacuum in order to avoid air bubbles being trapped in between the master and silicone. The surface quality and the dimensional accuracy of the master is a determining factor for the quality of vacuum casted components. After curing, the mold is cut according to the parting planes and the master is removed, leaving a cavity to make copies. To get more details, please refer another article: Vacuum Casting Process (https://www.dankemold.com/blog/vacuum-casting-process/)

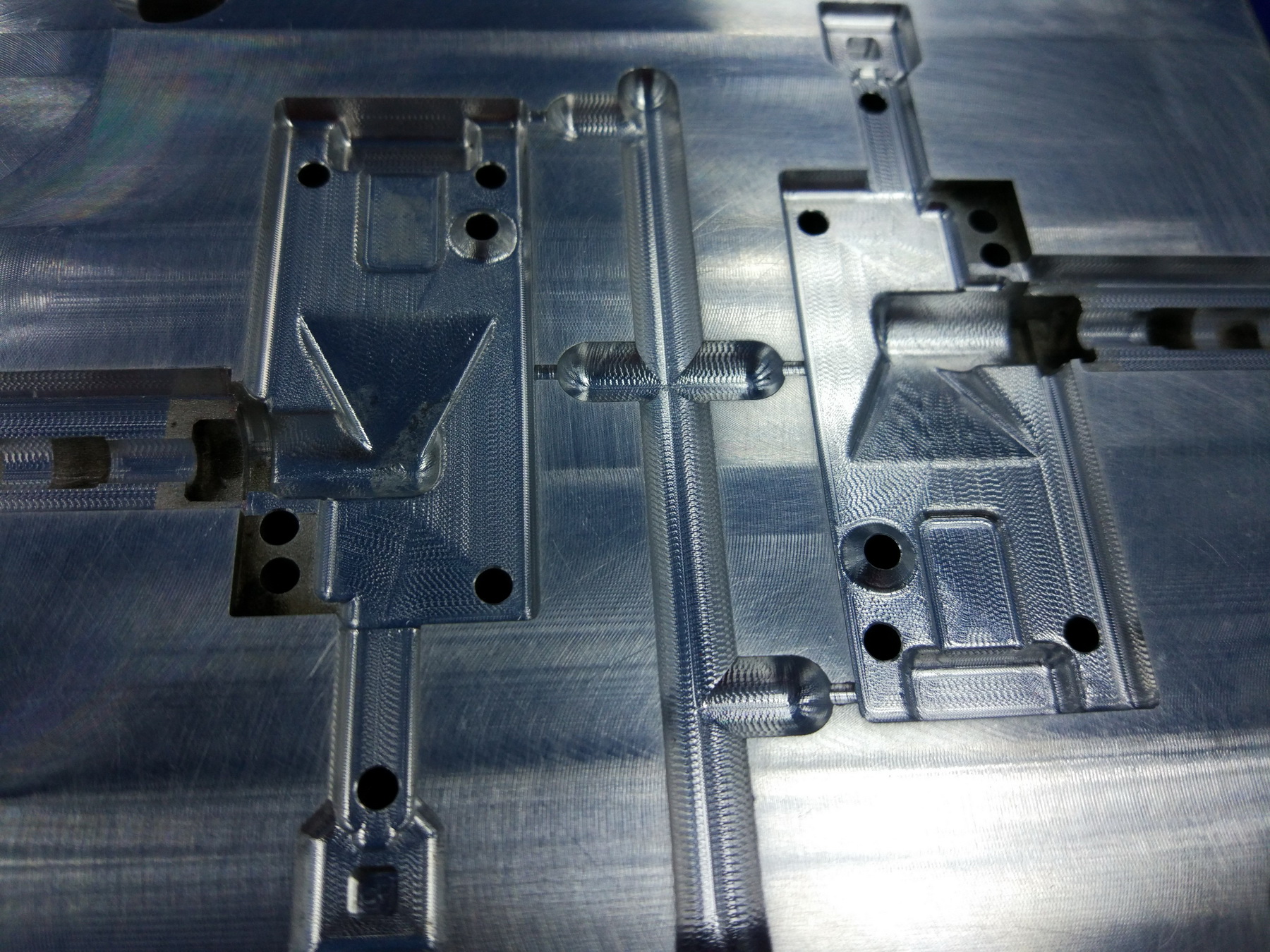
Soft metal tooling, usually is Aluminium tooling, the manufacturing method is almost the same as conventional steel tool, include CNC machining, EDM, wire-cutting, etc. However, aluminum tooling is more cost-effective to become more competitive, because the advantages are obviously, shorter lead-times on the tool build due to faster machining times, which also reduces costs, plus better thermal conductivity that can mean greatly reduced cycle times, etc.
About material of parts that aluminium tool produce, though it’s not rigid as steel, aluminium tooling can be very robust which enables us to mould in most thermoplastic materials, from polypropylene and ABS to high temperature metal replacement engineering polymers like PPS, PEEK,etc..
About lead-time, it depends on the complexity and how busy the factory is at any given time. We’ve produced simple non-complex tools and do injection moldings in a couple of days, to very complex tools and moldings in several weeks. It’s always best to contact us to discuss your requirements at the time.
About the cost of aluminium tooling, this also depends on the levels of complexity, but generally it’s around 30-40% cheaper. Since it also has much shorter lead times, which in itself offers reduced time to market for new products and the potential for substantial cost savings.
As for the quantity of parts that aluminum mold produce, this again depends on the levels of complexity. Usually, you can get from 50 parts for your functional or evaluation testing and 10,000+ parts for your marketing test. The average will depend on the demand.
There are several criteria will determine if vacuum casting or aluminum mold is suitable for an application. Part design/configuration and volume are the two major consideration. Sometimes, according to your requirement, we can even builds ‘hybrid’ molds that may be primarily steel but might incorporate aluminum inserts in a standing or deep-draw piece, or an area where it’s difficult to get water resulting in a hot area that will affect cycle or hurt quality. If you are still confused, we are pleased to be your consultant to choose the proper process and help you to accomplish your product development.
