Some practical notes about Rapid Prototyping-Sectioning
When we running rapid prototype projects, which I mean includes CNC machining, SLA and vacuum casting projects, there’s various of “rules” that we should know. These “rules” are actually indications to help us to avoid some mistake and save time/cost. Therefore, we have a series of articles to share some practical notes about rapid prototyping process. For this paper we would like to talk about “Sectioning”.
What does “Sectioning” mean?
Sectioning is an assisted manufacturing method that split the parts (3D data) into 2 or more pieces in 3D software, programme and machine them separately, then glue them together to build a complete part as per 3D drawing. It is usually adopted when machining some plastic parts, sometimes also available for metal parts because they can be welded, but it’s rare.
When we need or should use “sectioning” proposal for the parts we want to machine?
1)Parts with large size that exceed the maximum machined area of CNC machine, it can’t be machined in single pieces in the machine. For example, some housing parts or cover parts of car or home appliances.
2)Parts with closed and hollow structure, or other features that CNC cutter can’t achieve. Such as plastic bottles or boxes, and some parts with very deep holes, tiny grooves, undercuts, etc.
3)Parts with complex structures or need to be machined from many directions, and it’s only used for appearance checking or exhibition, but not functional test.
What’s the benefit from sectioning?
Frist of all, sectioning makes it easier when we make complicated parts which is difficult to be machined or even can’t be machined out at all. Such as some hollow bottles, parts with undercut features, etc.


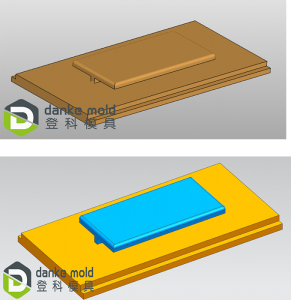
Secondly, sectioning saves much material compare to machining parts in single piece directly. For example, when we make a rectangular box, split it into 5 plates and machine them independently instead of digging the hollow space from a large block could save amount of material and reduce waste. Machining time is also shorter a lot accordingly.
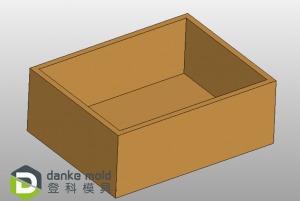
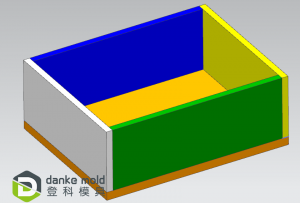
Last, sectioning makes surface treatment easier and more convenient. For example, when there’s an acrylic (PMMA) bottle (like the picture above) need to be polished to high glossy and transparent, it is very difficult, even impossible to do if the part made in a whole piece (Suppose it can be). Split the bottle, and polish each part to the request surface finish, then glue them up, that’s much easier.
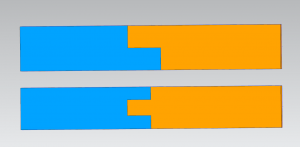
How does the joint of the two split part look like when section the parts?
In order to keep the structure of product as steady as possible, the joint of the two split part should never be just glued with flat sectioning face to face simply, but should buckle to each other just like the picture below:
What else should we consider when we decide to use “Sectioning” proposal?
1 Some material can’t be glued together after sectioning. For instance, PP, POM, PE, Nylon (/with Glass fiber), they are hard to glue because they have “low surface energy”. Very crudely, they have little interest in sticking to anything else, including adhesives.
2, Sectioning affect the strength and impact resistance of the part more or less even we are very careful, so we should not section those key position which is possible be under external force during using. And avoid to pick the features that affect the appearance as possible.
3 If the final product need to go through some special test, like water-tightness testing, high temperature resistance testing, corrosion preventive testing, etc. Sectioning is not recommended.
Danke Mold is experienced to make the optimal proposal for customers, to save their cost and time, and get high quality rapid prototypes. Besides, we also provide rapid tooling and injection molding service, please click www.dankemold.com to get more information.
