If you’re a startup looking to bring a product to market without committing to large quantities, low volume manufacturing offers a practical solution. This approach lets you produce smaller batches, reducing upfront costs while maintaining quality and flexibility.
Low volume manufacturing enables you to test your product, iterate quickly, and manage your budget efficiently in the early stages of your business. It’s tailored for startups that need to validate ideas or fulfill initial customer demand without the risks tied to mass production.
Choosing the right low volume production strategy can protect your resources and support rapid growth. Understanding how to leverage these manufacturing options can give your startup a competitive edge and help you move from concept to customer with less risk.
Foundations of Low Volume Production for Startups
Understanding how to manage production in smaller quantities can save you time and resources during your startup’s early phase. Efficiently balancing cost, quality, and flexibility is crucial for bringing your product to market without overcommitting capital.
Defining Low Volume Production
Low volume production refers to manufacturing a limited quantity of products, typically ranging from a few dozen to several thousand units. This approach contrasts with mass production, focusing on small batch sizes tailored to niche markets or product testing.
You engage in low volume manufacturing when your startup needs to validate product designs or respond quickly to market feedback. This method allows you to avoid significant upfront costs and inventory buildup while maintaining control over product quality and customization.
Benefits for Startup Development
By adopting low volume manufacturing, you minimize financial risk by producing only what your market demands. This cost-effective small-batch manufacturing allows you to test concepts and adjust designs based on honest user feedback.
You gain flexibility to pivot or improve products without being locked into significant inventory commitments. It also accelerates time to market, as setup and tooling costs are lower compared to high-volume runs.
Additionally, it supports building relationships with manufacturers that can scale alongside your company as demand grows.
Common Challenges and Solutions
You may face higher per-unit costs when producing low volumes due to a lack of economies of scale. To offset this, consider using modular designs or standard components to reduce customization expenses.
Supplier lead times can be unpredictable for small orders. Establish strong communication channels with your manufacturers and plan production schedules that include buffer times to minimize delays.
Quality consistency may vary because processes aren’t as optimized as in mass production. Implement rigorous quality control at every step and work closely with your production partners to ensure standards are met.
Practical Strategies and Implementation Methods
To succeed with low volume manufacturing, you must focus on precise and cost-effective methods that validate your product concept while managing risk. These strategies allow you to refine your product and scale efficiently without excess inventory or overhead.
MVP Prototyping Strategies
Your minimum viable product (MVP) should be designed with iteration and cost in mind. Utilize rapid prototyping techniques, such as 3D printing or CNC machining, to rapidly produce functional models that accurately reflect the core product features. This reduces upfront capital and speeds up feedback collection.
Focus on essential features only, avoiding over-engineering. Prioritize user functionality over aesthetics to test market reactions early. Early-stage prototypes don’t need to be perfect but must prove feasibility and gather actionable insights.
By integrating low volume manufacturing into MVP processes, you ensure faster turnaround and simpler transitions to small-scale production runs. This supports lean development cycles and tight budget control.
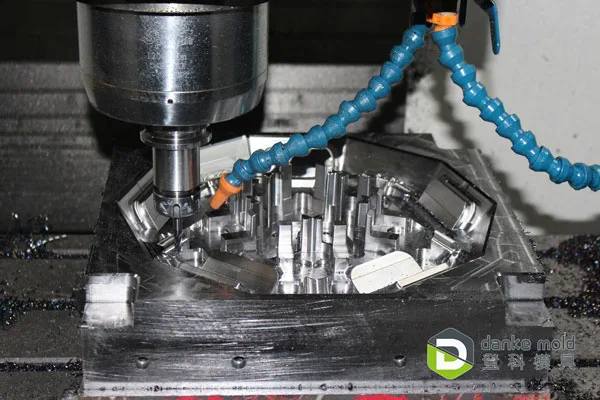
CNC machining
Lean Production for Market Validation
Lean production emphasizes minimizing waste and maximizing value, making it ideal for startups testing their product-market fit. You should produce only what is immediately needed based on customer demand or pre-orders to avoid excess inventory.
Implement pull-based systems where production aligns strictly with sales signals. This method reduces storage costs and lets you adapt quickly to customer feedback or market shifts.
Standardizing components and simplifying assembly processes enhances efficiency in low volume manufacturing environments. It also ensures your startup can pivot design or features without costly retooling, allowing for agile responses during market validation phases.
On-Demand Manufacturing Approaches
On-demand manufacturing enables you to produce goods only after an order is placed, thereby eliminating excess stock and reducing financial risk. Digital manufacturing techniques and partnerships with flexible suppliers are key to this approach.
You should leverage technologies like additive manufacturing or local machining to fulfill customized or small batch orders quickly. This supports scalable manufacturing for niche products by allowing variation without committing to extensive inventories.
Collaborate with manufacturers that specialize in low volume manufacturing and offer fast setup times. This enables you to test new designs in real market conditions with minimal lead times, keeping your capital tightly managed.
